Contraceptives
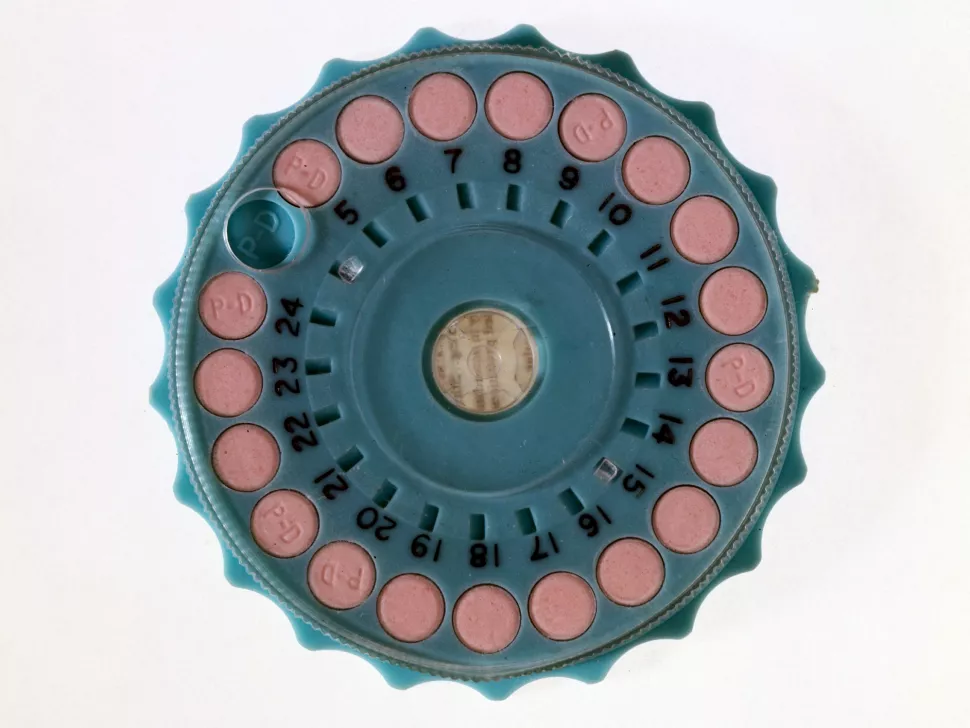

Birth control pills, condoms, and other contraceptives have not only encouraged men and women to engage in sexual activity for pleasure rather than reproduction in the developed world, but they have also significantly decreased the average number of children born to each woman in the nations where they are used. Modern families have greater standards of living and can better care for each child since there are fewer mouths to feed. Contraceptives are enabling the human population globally to level off, and by the end of the century, our population will likely have stabilized. The use of condoms and other contraception helps to stop the spread of STDs.
The use of natural and herbal contraception dates back thousands of years. According to researcher Jessica Borge’s book “Protective Practices: A History of the London Rubber Company and the Condom Business” (McGill-University Queen’s Press, 2020), condoms or “sheaths” have existed in some form or another since ancient times. The rubber condom was created in the 19th century. According to author Jonathan Eig’s book, “The Birth of the Pill: How Four Pioneers Reinvented Sex and Launched a Revolution,” the FDA authorized the first oral contraceptive pill in the US in 1960, and by 1965, more than 6.5 million American women were using it (W. W. Norton & Company, 2015).
Researchers are working to develop a male version of “the pill” as birth control technology advances.
The Food and Drug Administration approved Essure, a permanent birth control implant, in 2002, however the FDA cautioned in 2016 that the device would require stronger warnings to inform patients about significant risks associated with using Essure.
The Internet
Billions of people throughout the world utilize the internet, a global network of linked computer networks. The first version of the internet, known as ARPANET, was created in the 1960s by a group of computer scientists working for the ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) of the U.S. Defense Department. It made use of a data transfer technique called “packet switching,” created by team member and computer scientist Lawrence Roberts based on earlier work by other computer scientists.
According to computer scientist Harry R. Lewis’ book “Ideas That Created the Future: Classic Papers of Computer Science,” this technology was advanced in the 1970s by scientists Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn, who created the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP), two vital internet communication protocols (MIT Press, 2021). Kahn and Cerf are frequently referred to as the “inventors of the internet” because of this.
The World Wide Web, created by computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee while working at CERN in 1989, helped the internet advance (The European Organization for Nuclear Research). The fundamental concept behind the WWW, according to CERN, was to combine the rapidly developing fields of computers, data networks, and hypertext into a robust and user-friendly worldwide information system. The creation of the WWW united the world in a way that had never been possible before and made the internet accessible to everyone.








